If clauses. If Clauses 2020-01-31
Clause

When it is the subject or something embedded in the subject that is focused, however, subject-auxiliary inversion does not occur. We consider that a joke. Such argument clauses are content clauses: a. They are also prevalent, though, as relative pronouns, in which case they serve to introduce a relative clause and are not part of a question. We like the music that you brought. It is also called the real conditional because it reflect a realistic possibility. Relative clauses introduced by the relative pronoun that as in the b-clauses here have an outward appearance that is closely similar to that of content clauses.
Next
Conditional Clauses in English Grammar
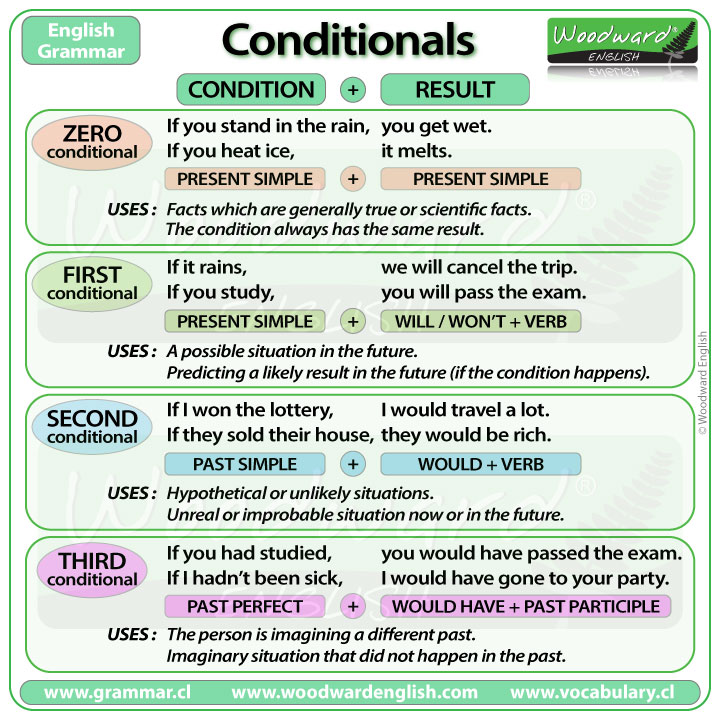
They have done the job. Adjunct clauses can also modify a nominal predicate. More complex sentences may contain multiple clauses. Fred arrived before you did. See und on how to form negative sentences. See for instance Crystal 1997:62.
Next
If Clauses

Subordinate clauses embedded clauses, are those that would be awkward or incomplete if they were alone. A typical clause consists of a and a , the latter typically a , a with any and other modifiers. Larry sent Susan to the store. The embedded wh-clause what we want is the object argument of the predicate know. Form if + Simple Present, will-Future Example: If I find her address, I will send her an invitation. The choice of labels was influenced by the theory-internal desire to use the labels consistently. Had they done the job,.
Next
If Clause Type 1

He became what he always wanted to be. A typical small clause consists of a noun phrase and a predicative expression, e. If Clauses — Type 1 is used to express a possibility in the future It is not certain that it will happen, but it is possible. Clauses can be, however, embedded inside phrases. The other is called the Main clause.
Next
Conditional Clauses in English Grammar

Main clauses matrix clauses, are those that can stand alone as a sentence. The third conditional express an impossible condition — we cannot go back in time to change the outcome of these conditions. The predicate in question is usually the matrix predicate of a main clause, but embedding of predicates is also frequent. It should be apparent that non-finite clauses are by and large embedded clauses. Wh-words often serve to help express a constituent question. When they function as nouns as in the b-sentences, it is debatable whether they constitute clauses, since nouns are not generally taken to be constitutive of clauses.
Next
If

The arrow dependency edges identify them as adjuncts. They can also modify a noun predicate, in which case they are known as. Other theories of syntax and grammar e. But I have to do my homework. They consist of a main clause and a conditional dependent clause.
Next
Clause

Both of these argument clauses are directly dependent on the main verb of the matrix clause. A more traditional understanding of clauses and phrases maintains that phrases are not clauses, and clauses are not phrases. However, using other verbs will change the meaning of the sentence. Subject-auxiliary inversion is obligatory in matrix clauses when something other than the subject is focused, but it never occurs in embedded clauses regardless of the constituent that is focused. We've heard about Susan attempting a solution. This confusion is due in part to how these concepts are employed in the of the Chomskyan tradition. He attempted to explain his concerns.
Next
Clause

That was when they laughed. Some theories of syntax posit the null subject i. The acknowledged at least three projection levels for every lexical head: a minimal projection e. It is important to know which tenses are to be used in these clauses and they play a big role in determining the meaning of the sentence. Notes on Sentence Structure We change the order of the two clauses.
Next
If Clause Type 1
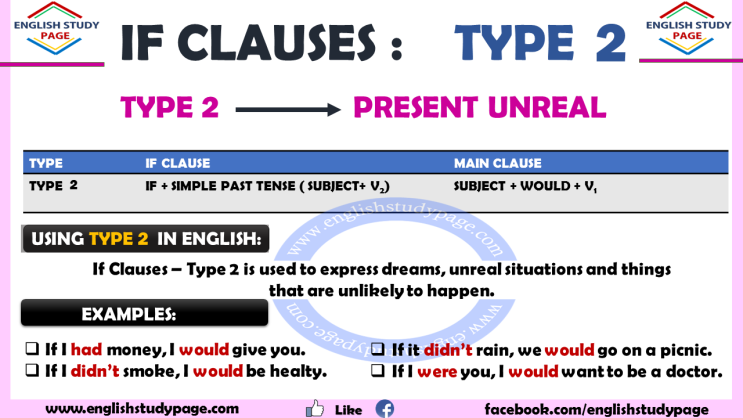
Traditional grammar focuses on finite clauses, the awareness of non-finite clauses having arisen much later in connection with the modern study of syntax. Someone is wondering where Larry sent Susan. Conditional clauses are often introduced by the word if, although, sometimes other words can be used see: and. While the subject-predicate relationship is indisputably present, the underlined strings do not behave as single , a fact that undermines their status as clauses. The characteristic trait of clauses, i.
Next
Clause
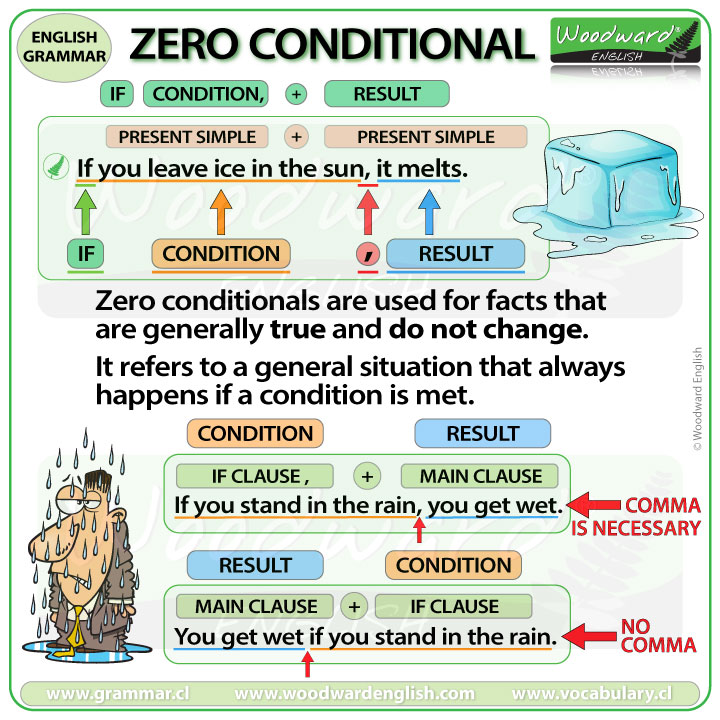
The typical instance of this type of adjunct is a relative clause, e. Have they done the job? Learn more about and usage in the section of the website. The first is a dependent of the main verb of the matrix clause and the second is a dependent of the object noun. That they actually helped was really appreciated. They seem to straddle two syntactic categories: they can function as non-finite verbs or as nouns.
Next









