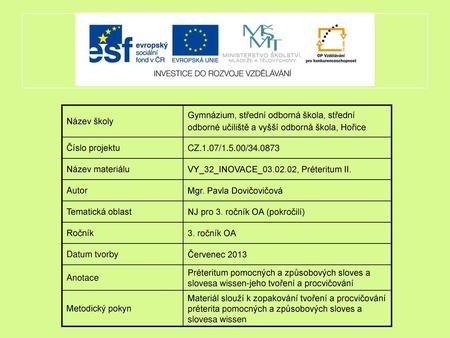
Preteritum. Verbets tempus 2019-11-30
Imperfekt
Er lud uns dieses Mal nicht ein. Now, this does not imply that Präteritum is the past tense used in written form whereas Perfekt is the kind of informal spoken form of it. Berichten, drückt das Präteritum Handlungen und Vorgänge aus, die in der Vergangenheit abgeschlossen wurden und keinen unmittelbaren Bezug zur Gegenwart haben. Det är min dröm att dessa arbeten skall hjälpa människor med den svenska grammatiken och öka intresset för läsandet och skrivandet i Sverige. Further, I am inclined to encourage you to speak German in every situation. A story in that sense is anything which is remote. Du har chansen att nå många läsare då tusentals besöker dessa sidor varje dag.
Next
Preterite
Additionally, you need to conjugate the imperfect verb form according to person and number. Usually in spoken language there is no differentiation between Präteritum and Perfekt. Övningsuppgift Skriv ner meningar och använd olika verb som står i futurum. Typical conjugations with the word sein to be are: Ind. In English it can be used to refer to the verb form, which sometimes but not always expresses perfective aspect.
Next
Préteritum

Since I have been learning English as a second language myself for almost 20 years now I know how difficult it is to learn a language other than your native one. Man kan även använda presens och ange att något kommer att ske i framtiden: Exempel: I morgon reser jag till Spanien. Wann verwendet man Präteritum im Deutschen? Strong, or irregular, verbs generally change the vowel in the stressed syllable. Han har vistats utomlands i 10 år och han trivs mycket bra. It is rather used as a literary language. Beispiel: Im letzten Jahr habe ich Urlaub in Deutschland gemacht. Thus, I am always willing to keep my explanations about German grammar comprehensible and short.
Next
Präteritum/Imperfekt

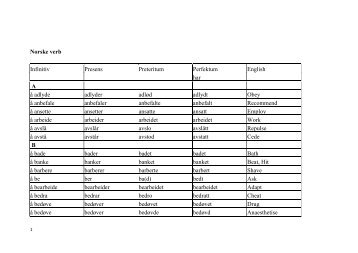
Måste säga att jag tycker din sida är grymt bra och innehållsrik, gillar den starkt! In Schriftform wird das noch unterschieden, im Gespräch nicht. Usually, a definite start time or end time for the action is stated. Weak verbs form the simple past by adding - e te, - e test, - e ten, or - e tet to the stem: Ich sagte das. Person Plural ihr ihr wart ihr hattet 3. Övningsuppgift Skriv ner meningar och använd olika verb som står i konditionalis1. Imperfekt eller preteritum Detta tempus kallades tidigare imperfekt i svenskan men kallas numera preteritum. In the 3rd person singular, both bäckt and backt are possible.
Next
Präteritum (német elbeszélő múlt)

The perfect in Latin also functions in other circumstances as a. Jag trodde nog också att ändelsen hade med latinet att göra. Whether Perfekt or Präteritum is used depends more on whether the sentence is spoken or written than on when the action is completed. Er rief seine Mutter nie an. I talt norsk og radikalt bokmål brukes mest -a i stedet for -et. Är du intresserad av att publicera en dikt, artikel, novell eller berättelse på dessa sidor? Tvoření je buď pravidelné nebo nepravidelné.
Next
Präteritum/Imperfekt

A volte si sono anche divertiti. Kanske du vill publicera dig och börja din bana som författare här! The case of is similar: the Präteritum is the simple non-compound past tense, which does not always imply perfective aspect, and is anyway often replaced by the Perfekt compound past even in perfective past meanings. In einer Bewerbung wird man diesen Satz nicht finden, da der Bezug zur Gegenwart wichtig ist, selbst wenn der Vorgang schon länger zurückliegt. Person Singular du -test du lern test -st du sah st 3. Traditional Spanish terminology calls all past tenses pretéritos, irrespective of whether they express completed or incomplete actions or events. The latter is used when something happened and was finished in the past but is still effective.
Next
Imperfekt och preteritum

Erich Romann lived here until 1935, when, under pressure from the Nazi regime, he took his own life Further distinctions between the simple past and the present perfect: in spoken German, the simple past is perceived as formal. Grunden i min pedagogik är att gå till grunden och förklara allt så enkelt och klart som möjligt - och sedan lägga till många exempel som visar användningen. Jahrhunderts in der nichtmundartlichen Umgangssprache auch in Norddeutschland das Perfekt aus, was mit einem gleichzeitigen Rückgang der traditionellen Mundarten in diesen Regionen einhergeht. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Sie kam en immer zu spät. Vegyes igék denken senden 1 wissen ich -te dachte sandte wusste du -te st dachtest sandtest wusstest er -te dachte sandte wusste wir -te n dachten sandten wussten ihr -te t dachtet sandtet wusstet sie -te n dachten sandten wussten Az elbeszélő múlt Präteritum használata Er eröffnete die Konferenz und erklärte.
Next
Preterit u nemačkom jeziku

. The general tendency is to use the compound past perfectul compus to express a past action that is perceived as completed at the moment of speaking. Riceverai nella tua posta regole della grammatica, esercizi e vocaboli in piccole porzioni oltre a qualche curiosità sulla lingua e le abitudini. Původní funkcí německého préterita bylo označení prostého minulého děje bez jakéhokoliv zřetele k současnosti nebo vidového rozlišení, což jej předurčovalo k použití zejména jako času vyprávěcího. She had two children who were like the two rose-trees, and one was called Snow White, and the other Rose Red. In ordinary conversation, then, the simple past is unusual.
Next
I verbi al Präteritum nella lingua tedesca

Nor does it mean that one needs to convert a spoken Perfekt to Präteritum when writing it or use Perfect when re-telling a scary novel at a campfire. Perfekt används även för att uttrycka att något har inträffat nyligen. Sie brachte ihren neuen Freund mit. As a result, ordinary speakers have forgotten the preterite form of some strong verbs that are traditionally used informally. Spesso portavate dolciumi ai bambini. Person Plural ihr -tet ihr lern tet -t ihr sah t 3.
Next







