Private equity. Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect 2020-02-02
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

If all of a public company is bought, it results in a delisting of that company on the stock exchange. Since interest rates are so low, they borrow funds to make a new investment. Since private equity investments have a longer time horizon than typical stock investors, private equity can be used to fund new technologies, make acquisitions, or strengthen a balance sheet and provide more working. After holding the investment for a while, they use investors' cash to pay off the loan and take ownership of the asset when it looks like the investment is about to pay back. These private stakes in a company are usually bought by private equity firms. Private equity investors can buy all or part of a private or public company, and they usually have a 5 to 10-year time horizon for which they want to keep their investment before selling.
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

As a result, it looks like the investors received a huge return in a short period. Because of this, the banks didn't care if the loans were good or not. The funds typically have annual extensions, and the money comes mainly from institutional investors, like pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and corporate cash managers, as well as family trust funds and even wealthy individuals. Firms can keep the holdings, or sell these stakes to private investors, institutional investors government and pension funds , and. Source: Prequin, Private Equity Spotlight October 2007. In addition, private equity financing allowed corporations to buy back their own shares, also driving remaining share prices up.
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect
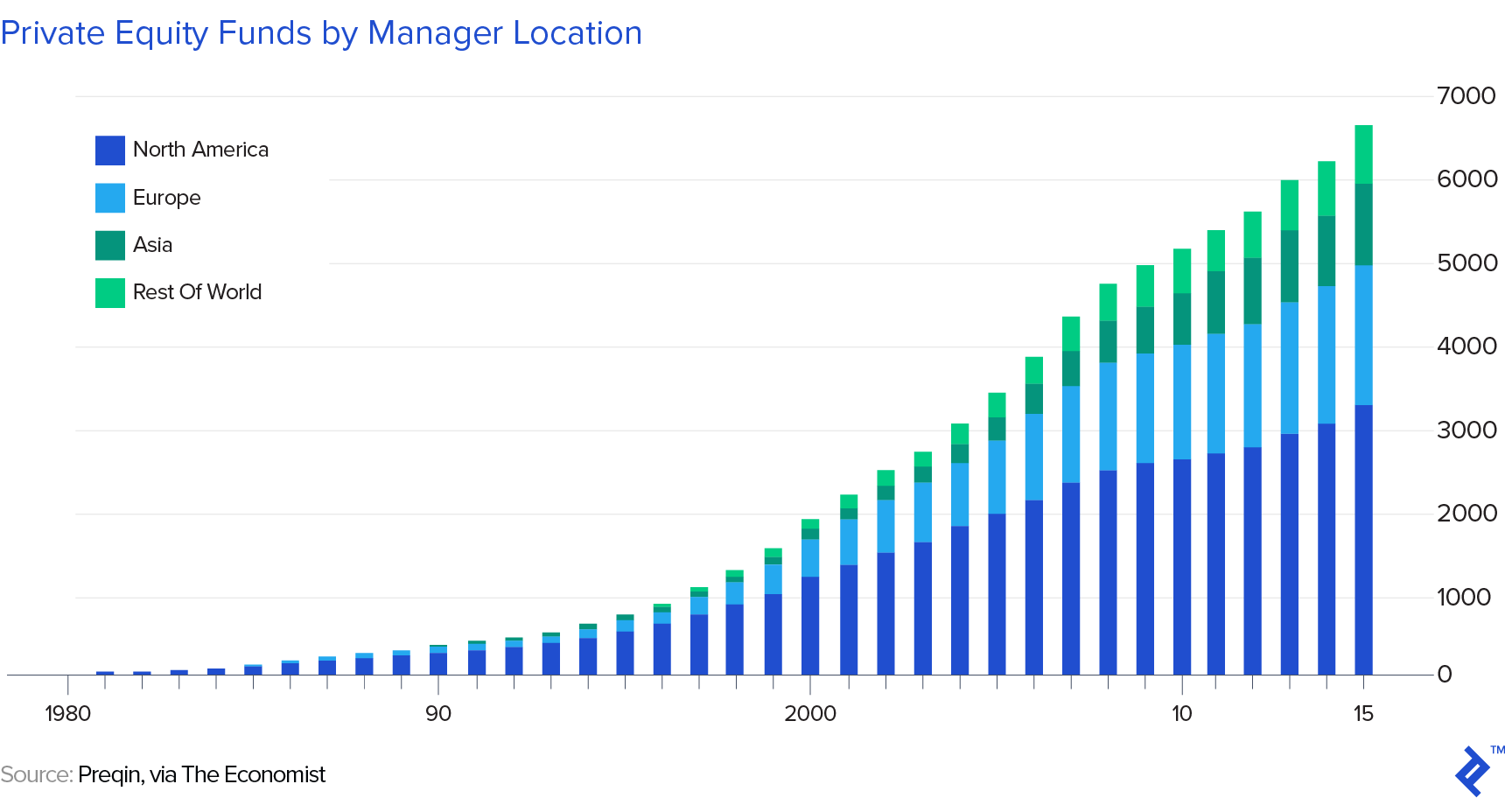
The excess created by private equity was one of the causes of the and subsequent recession. Private equity investors hope to beat the market in the long run by selling their ownership at a great profit either through an or to a large public company. Private equity firms can either be privately held, or a public company listed on a stock exchange. That's because private equity investors are willing to wait longer to obtain a higher return, while stock market investors generally want a return that quarter if not sooner. . It can include cash and loans, but not stocks or.
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect
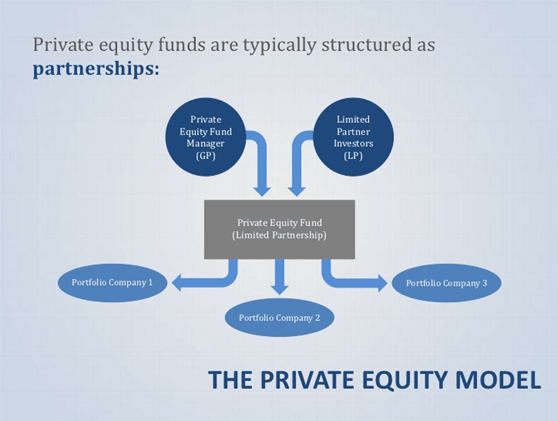
This additional capital took many public corporations off the stock market, thus driving up the share prices of those that were left. In addition, the impact of these loans going sour was felt in all financial sectors, not just banks. Many of the loans that banks make to the private equity funds were then sold as. Private equity is private ownership, as opposed to , of a company. These funds are usually structured as limited partnerships, with a duration of 10 years.
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

. . . . . . .
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

. . . . . .
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

. . . . .
Next
Private Equity: Definition, Firms, Funds, Effect

. . . . . .
Next







