Salmonella. Salmonella Infections: MedlinePlus 2019-12-19
Treatment for Salmonella Infection

Prevention Many precautions can help prevent salmonellosis, according to the U. Aseptically weigh 25 g sample into sterile, wide-mouth, screw-cap jar 500 ml or other appropriate container. In this system the Ewing scheme many strains familiarly named as species are designated as serotypes of S. Since occasional uninoculated tubes of malonate broth turn blue positive test on standing, include uninoculated tube of this broth as control. Cap jar securely and let stand 60 ± 5 min at room temperature. Incubate 24 ± 2 h at 35°C.
Next
Sam O'Nella Academy
Add 225 ml sterile and 2. The Food and Drug Administration also indicates that some salmonella outbreaks have been traced to contaminants in spices. Continue as in , below. Adjust pH, if necessary, to 6. Aseptically transfer homogenized mixture to sterile, wide-mouth, screw-cap jar 500 ml or other appropriate container and let stand 60 ± 5 min at room temperature with jar securely capped. Preventive methods are especially important when preparing food or providing care for infants, older adults and people with weakened immune systems.
Next
Treatment for Salmonella Infection

The illness usually lasts 4 to 7 days, and most persons recover without treatment. Place rabbit carcass into sterile plastic bag. For laked dyes or dyes with pH below 6. For example, if 225 ml lactose broth is added, the maximum volume of added surfactant is 2. Perform Spicer-Edwards flagellar H antisera test as described in , above.
Next
Salmonella infection
Aseptically weigh 25 g into a sterile wide mouth Erlenmeyer flask or other appropriate container. Could I have caught Salmonella? Place the mango into a sterile plastic bag. If cultures are not motile after the first 24 h, incubate an additional 24 h at 35°C; if still not motile, incubate up to 5 days at 25°C. Nontyphoidal salmonella: Gastrointestinal infection and carriage. For Triton X-100 this quantity may be as little as 2 or 3 drops. Polyvalent flagellar test agglutination no agglutination + 11.
Next
Salmonella Infections: MedlinePlus

The term Salmonella refers to a group of bacteria that cause Salmonella infection, or salmonellosis, in the intestinal tract. Mix well and let stand 60 ± 5 min at room temperature with jar securely capped. Remove any adherent material from the egg shell surface. Add 225 ml without brilliant green dye. More detail is in the main article. Contamination typically happens after infected feces comes into contact with animals, crops or water and people then consume or touch those items and don't wash their hands. Food can also become contaminated when people improperly handle it, by failing to thoroughly wash their hands after using the toilet, changing a diaper or touching a contaminated surface.
Next
Treatment for Salmonella Infection
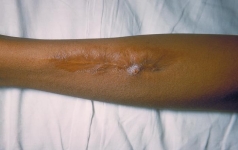
They are especially important in preventing food poisoning. About half of the strains are known to cause in humans. This method is used for all domestic and imported rabbit carcasses. Observe at 15 min intervals and read final results in 1 h. In the United States, it is a common cause of. Polyvalent somatic test agglutination no agglutination + 12. Salmonella poisoning is often linked to contaminated water or foods, especially meat, poultry, and eggs.
Next
Salmonella

The second change involves the option of refrigerating incubated preenrichments and selective enrichments of low-moisture foods for up to 72 h. While all serotypes can cause disease in humans, a few are host-specific and can reside in only one or a few animal species: for example, Salmonella enterica serotype Dublin in cattle and Salmonella enterica serotype Choleraesuis in pigs. En Estados Unidos es la causa más común de las. The agency is seeking ways to increase the safety of spices. Clinical laboratories frequently report salmonellae as one of three species, differentiated on the basis of serologic and biochemical reactions: S.
Next
Salmonella (non
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-salmonella-770636-01-14bd4f0606904ad6baa8c1c2486875be.png)
More than 7,000 cases of Salmonella were confirmed in 2009; however the majority of cases go unreported. If frozen, sample must be tempered to obtain analytical portion. Relative effectiveness of selenite cystine broth, tetrathionate broth, and Rappaport-Vassiliadis medium for the recovery of Salmonella from raw flesh, highly contaminated foods, and poultry feed: Collaborative study. They are pathogenic for humans and other animals. Mix well by swirling and determine pH with test paper.
Next
What Is Salmonella?

After 96 ± 2 h, add 3,375 ml sterile , as described above, and mix well by swirling. Perform the following additional tests on cultures that do not give typical Salmonella reactions for tests 1-11 in and that consequently do not classify as Salmonella. . Harvesting seafood in contaminated waters is a common cause. Egg contents yolk and albumen are thoroughly mixed before analysis. Incubate 24 ± 2 h at 35°C.
Next
Treatment for Salmonella Infection
Add 225 ml without ferrous sulfate and mix well by swirling. Aseptically weigh 25 g sample into sterile, wide-mouth, screw-cap jar 500 ml or other appropriate container. Antimicrobials are also administered if the infection spreads from the intestine to other body parts. Adjust pH, if necessary, to 6. Salmonella infection usually occurs when a person eats food contaminated with the feces of animals or humans carrying the bacteria.
Next







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-salmonella-770636-01-14bd4f0606904ad6baa8c1c2486875be.png)

