Sextaner definition. Secant of a circle definition 2019-11-21
Sextaner

These items are so named because their arcs describe a quarter circle, fifth of a circle, and eighth of a circle, respectively. Local solar noon is when the sun is highest. Instruments The astrolab and octant are the predecessors of the sextant. If your sextant reads the horizon angle as greater than 0 a positive number , subtract the horizon angle from the angle measure of the object. Sight the horizon by looking through the horizon mirror. This correction factor is available from the Nautical Almanac.
Next
How to Use a Sextant: 14 Steps (with Pictures)

Any more than we will need sextant. If the sun appears south of you at an elevation angle of 49 degrees, subtract 49 from 90 to produce a difference of 41. Its primary use is to determine the angle between a celestial object and the horizon which is known as the object's altitude. With Reverso you can find the French translation, definition or synonym for sextant and thousands of other words. If you have trouble spotting it, there are two ways to find it. Bien caché dans la constitution d'un sextant.
Next
Sextant

Likewise, if the latitude at which the sun is directly overhead is north of the equator and the sun appears to your north at its highest point, you would subtract the latitude from the remaining angle to get your latitude. If you are between the tropics, the sun may appear either to your north or south at its highest point, or directly overhead, given the time of year. Find your elevation in feet if in meters, multiply by 3. It differs from the navigational sextant in that it is a much larger instrument and does not use mirrors to measure angles, thus meaning that it cannot measure angles any greater than its 60-degree arc. The navigator sees the horizon through the clear glass and a reflection of the observed body in the mirror. Common uses of the sextant include sighting the sun at solar noon and sighting Polaris at night, to find one's latitude.
Next
Sextant dictionary definition

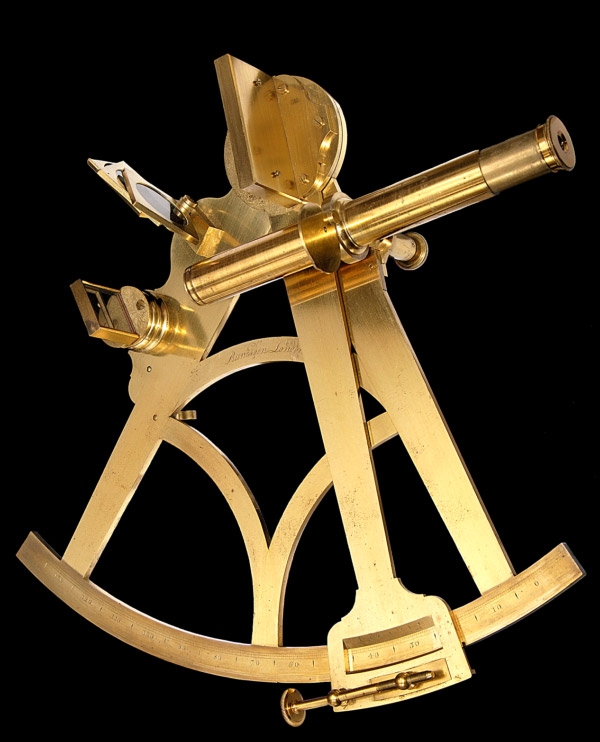
A horizontally mounted telescope and two small mirrors are arranged so that the observer can, by moving the pivoted arm, sight the horizon and the reflected image of the celestial body in the same line, giving a reading along the arc that is used to look up the observer's position in a published table. To learn how to find your latitude with the sextant, read on! The horizon mirror is only partially silvered, allowing you to look through it and through the sighting scope beyond it. With a marine sextant, a navigator can measure the altitudes of the sun and stars. You can get the correct refraction correction for where you are by consulting the Nautical Almanac. The angle of elevation for Polaris will be the same as your latitude. Another sextant model used a mirror to reflect the horizon alone.
Next
sextant

Clamp the index arm in place with the flip-lock, then turn the micrometer knob to fine-tune the sextant so the object is perfectly aligned with the horizon. Rotate the micrometer knob tangent screw back and forth so that you see both the star and its reflected image. Origin: From sextans, a bronze coin worth one-sixth of an as. See for a detailed explanation. If your sextant reads the horizon angle as less than 0 a negative number , add the number of degrees difference to the angle measure of the object.
Next
What does sextant mean? definition, meaning and audio pronunciation (Free English Language Dictionary)

To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time. Instruments L'astrolabe et l'octant sont les ancêtres du sextant. Polaris is the brightest star in the constellation Ursa Minor the Little Bear, Little Dipper. If the sun appeared overhead at a latitude of 20 degrees North latitude when you saw it at an elevation of 49 degrees from your position, your latitude would be 61 degrees North latitude 90 — 49 + 20. This is a problem only with antique sextants; modern ones use adjustable telescopes.
Next
Sextans
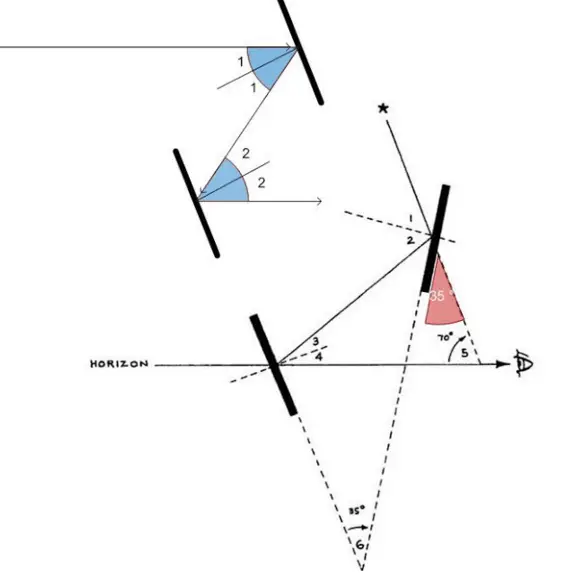
This correction adjusts for your position above sea level. The star will appear to dim to 10. If the reflected image passes directly through the actual image, your horizon mirror is aligned correctly. Although its design looks complicated, with an understanding of how it works and practice, you can reliably use it to find your position. Find the difference between the elevation angle of the sun and the zenith.
Next
Extranet
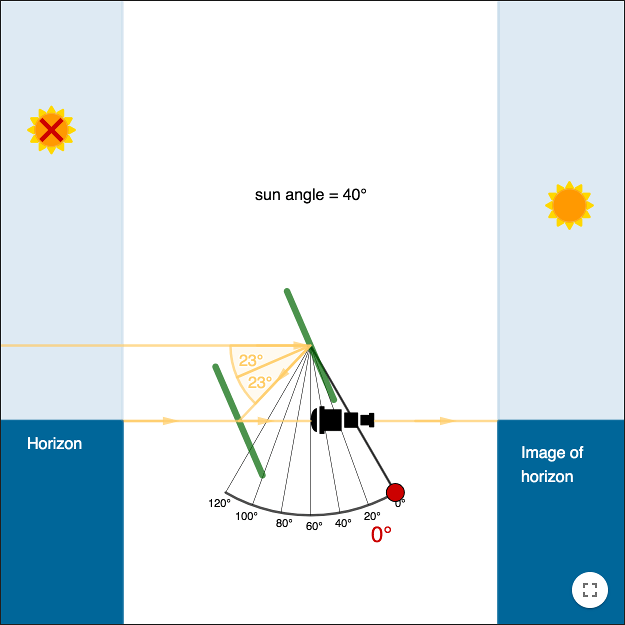
Un autre modèle de sextant utilisait un miroir pour refléter seulement l'horizon. . Other definitions In trigonometry, the secant of an angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the adjacent side. You can check for this by locking the index arm at 60 degrees and looking through the index mirror. Light rays bend when passing through a substance; this bending is called refraction.
Next
How to Use a Sextant: 14 Steps (with Pictures)

If the sun had appeared north of you at this same elevation on either of the equinoxes, your latitude would be 41 degrees South latitude. You can complete the translation of sextant given by the French-English Collins dictionary with other dictionaries such as: Wikipedia, Lexilogos, Larousse dictionary, Le Robert, Oxford, Grévisse. If it passes to one side, you have side error and must adjust the horizon mirror until the images pass through each other. Intersecting Secants As shown in the figure on the right, when two secants intersect at a point outside the circle, there is an interesting relationship between the line segments thus formed. Move the sextant so the stars move to one side of your field of view. Record the time you made your sighting in hours, minutes, and seconds, then record the angle measure, which you can find on the index bar, and correct for your elevation if necessary.
Next
Extranet

Find Polaris, the North Star. If the two points coincide at the same point, the secant becomes a , since it now touches the circle at just one point. Some also feature artificial horizons for use in conditions when a natural horizon cannot be seen. The line segment inside the circle between P and Q is called a. Moving the arm rotates the disk the index mirror is on until light hitting the index mirror hits the reflective portion of the horizon mirror, making the object the light comes from appear to rest on the horizon.
Next









