Which is bigger mb or kb. File Sizes Conversion GB MB KB Bytes Gigabyte Megabyte Kilobyte 2020-01-22
Which is bigger MB or KB

Text is one of the most naturally compact types of data at about one byte required to store each letter. Conversely, and newer represent this as 66 kB, rounding to the nearest 1000 bytes. The internationally recommended unit symbol for the kilobyte is kB. Again, this is a security thing also. It is also consistent with the other uses of the in computing, such as or. Gigahertz - Speed, not Bytes One gigahertz is 1 billion cycles per second a megahertz is a million cycles per second.
Next
Kilobyte
A song, a music file, can be anywhere from two to six or eight megabytes. Basic plan: before adding measures X and Y, convert them to be in the same units. A byte is the smallest unit of data which can be processed on any computer. A three page word document is approximately 30 kilobytes or 3000 bytes. Each bit denotes the binary value of either 1 or 0, which are interpreted as binary digits. A perfect example of an external hard drive is this one built by Maxtor.
Next
Which one is bigger KB or MB?

This particular flash drive is an eight gigabyte flash drive and I do not think they make them bigger than a 16 gigabyte these days but again, this stuff is just getting bigger by the day. The unit symbol is kB. A unit of digital information in computing and telecommunication is called a byte. Note, many non-alphanumeric characters such as symbols and foreign language characters use multiple bytes. The only time this becomes really important is when you are trying to back things up or move them.
Next
Which is Bigger
Therefore, one megabyte is one million bytes of information. The same happens when you go up from megabytes to gigabytes. Currently, hard drives and camera memory are being measured in gigabytes. Hence, it is the basic addressable element in many computer architectures. The correspondence between these values of 0 and 1 and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention. These prefixes are now part of the.
Next
Megabyte

Bytes are pieces of information and a file is made up of bytes. It maintains the integrity of the equipment because you do not want these pieces to fail. For example, to store the letter 'R' uses 1 byte, which is stored by the computer as 8 bits, '01010010'. Kilobytes Megabytes Gigabytes Terabytes The size of information in the computer is measured in kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes. A kilobyte represented in binary is 1024 bytes and is represented as 2 10. This definition is used in contexts and most , particularly , -based storage, and , and is also consistent with the other uses of the in computing, such as or. This definition is synonymous with the unambiguous binary prefix.
Next
Which one is bigger KB or MB?

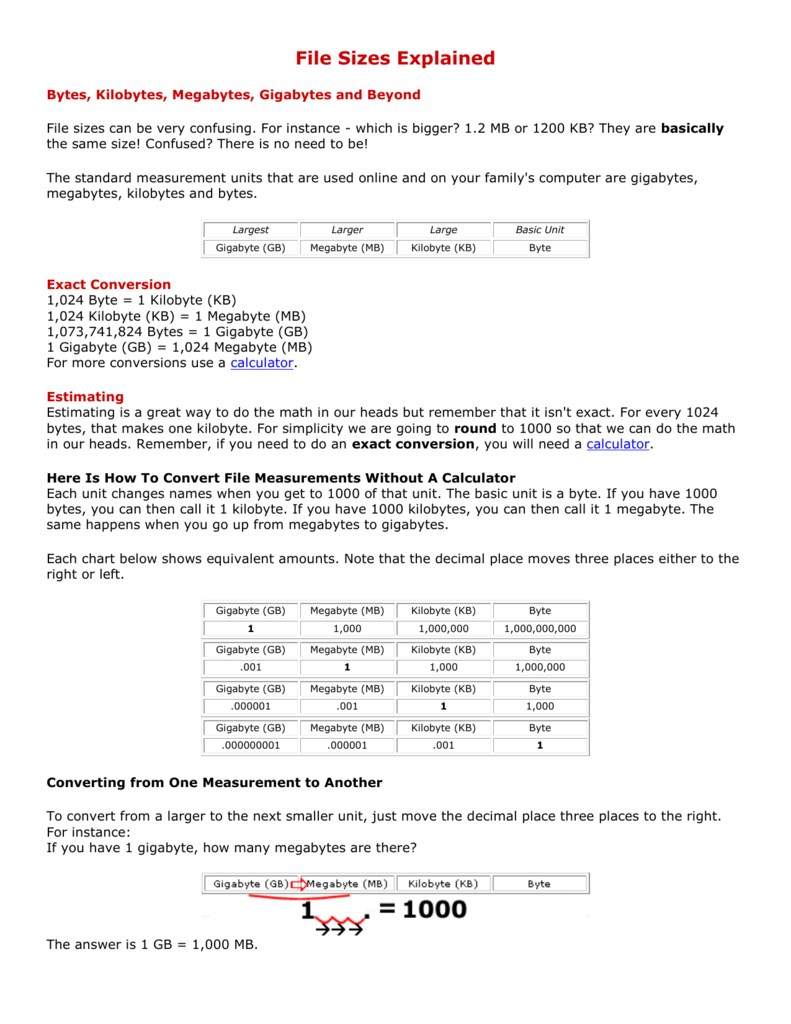
A megabyte is a 1000 kilobytes. The measurement Terabyte is starting to be heard more often. The basic unit is a byte. And a terabyte is a 1000 gigabytes. This free script provided by Estimate File Sizes That still doesn't help a whole lot unless you come back to this page and use a calculator. The answer is no because it is more than a megabyte. Note that the decimal place moves three places either to the right or left.
Next
What are KB, MB, GB, and TB? (Computer Tech 101)
If you have 1000 bytes, you can then call it 1 kilobyte. Imagine that each pit is interpreted as a 0, and the lack of a pit is a 1 as the spiral sequence is read. I generally recommend that if you have an enormous amount of information or more than will comfortably fit on an 8 megabyte flash drive that you do move into an external hard drive. However, in the decimal system, it stands for 1,000,000 bytes or 10 6 bytes. There is an easy way to estimate between file sizes. Soon, we will be going to even bigger units of measurement.
Next
Which is Bigger

Again, a three page document has approximately 30 kilobytes. In some areas of , particularly in reference to digital memory capacity, kilobyte instead denotes 1024 2 10 bytes. We'll talk about how compression works later. Since , file sizes are reported in decimal units. A single letter or character would use one byte of memory 8 bits , two characters would use two bytes 16 bits.
Next







