Yield curve inversion. The yield curve inverted — here are 5 things investors need to know 2020-01-30
The Yield Curve Has Inverted. What Does That Mean?

Eventually, the United States found itself thrown into a recession after the housing market crash roughly two years later. They know that the Federal Reserve lowers the when the economy slows. They feel confident putting their money into other sectors like mortgages and business loans, so Treasuries have to pay higher interest to compete. They can buy or sell on the open market. Thus, even if we take this yield curve inversion really seriously and I still have some serious doubts! This relationship becomes clear when an inverted yield curve precedes a recession. Consistent with a false alarm a la 1998. This is all about risk management.
Next
Inverted yield curve: Why the yield is fueling recession worries

They employ monetary policy to promote full employment and limit inflation. The bond market appears to be forecasting a future recession. As the economic cycle begins to slow, perhaps due to interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve Bank, the upward slope of the yield curve tends to flatten as short-term rates increase and longer yields stay stable or decline slightly. An inversion is when the short-term rates are higher than the long-term rates. Many past recessions have been caused by Fed tightening cycles.
Next
4 Times There Was an Inverted Yield Curve (And What Happened to Stocks)
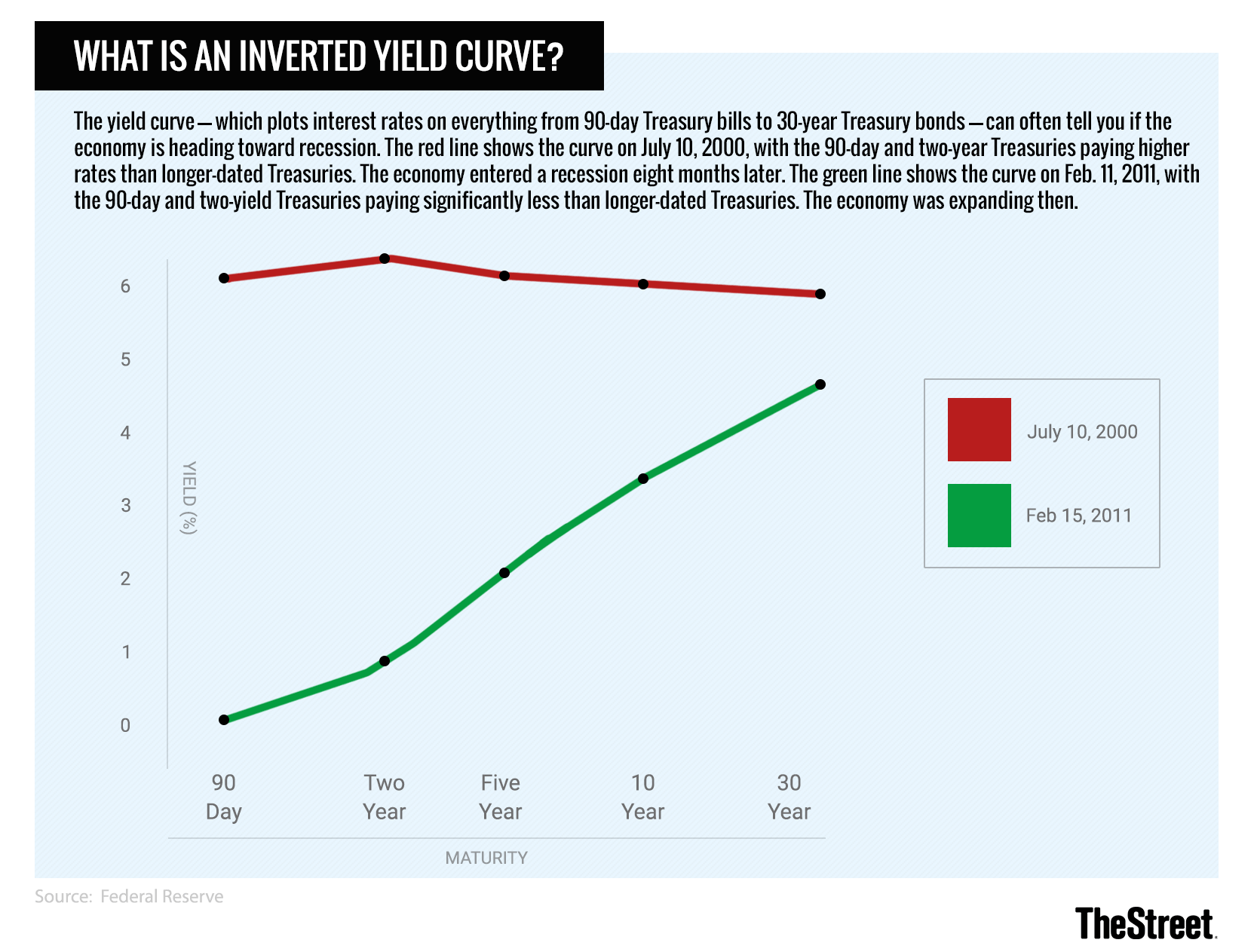
Mainly, they were aware that there was a growing within certain assets like housing, and they were concerned that low interest rates were causing this. Is an inversion a predictor of a recession? Treasury bonds, or bonds guaranteed to investors by the U. An inversion can mean that investors see more risk in the short run than the long run. You raise a lot of good points. Actually, the 1998 event is a bit reminiscent of the one in March this year: A very short and shallow yield curve inversion. Investors turn to bonds when stocks see increased volatility.
Next
NPR Choice page

Basically, investors have gotten too enthusiastic and are paying more than the underlying assets are worth. On average, markets rally about 15% after the yield-curve inversion. I have a largish portfolio and large expenses and query if I would sit there year after year. This is logical: the longer you put your money out, the more you want in return. After all, the yield curve inverted roughly 14 months before each of the past nine U. That was below the 1-year note yield of 1.
Next
Inverted Yield Curve Definition

About 18 months prior, the yield curve started flashing recession warning signs when the 10-year Treasury rate dropped below the two-year Treasury rate in June 1998. Something that will push future interest rates down low enough to justify long-term yields being low despite the risks. An inverted yield curve is almost guaranteed to spook investors. Higher yields on longer-term securities are a result of the maturity. Bear markets have actually happened every three years or so since 1900. But not every recession is the same, and there's no guarantee that the next downturn will cause foreclosures or another kind of financial loss. That's if people want to trade.
Next
The yield curve is inverted. Here's what that means, and what the implications are for the economy.
.1566488000880.png)
Treasury bond to yield 4. One takeaway for investors is that the inverted yield curve suggests a more near-term development than a recession: Interest rate cuts from the Federal Reserve. Layoff announcements have already , particularly in the auto industry. When the yields for long-term bonds fall far enough, it produces an inverted yield curve. In this environment, investors see long-term yields as an acceptable substitute for the potential of lower returns in equities and other asset classes, which tend to increase bond prices and reduce yields. It always goes like this: The Fed tries to fight inflation perceived or actual by raising interest rates to cool down the economy. For a few weeks, Treasury bond prices surged after the Russian debt default.
Next
What Does 'Inverted Yield Curve' Mean?

So for the curve to invert implies that investors are forecasting that something unusual will happen. They know that with a short-term bill, they have to reinvest that money in a few months. A powerful recession early warning signal 1970-2018! To learn how to make more money, you can download my. Indeed, just as the fancy hedge fund managers and algorithmic traders are aware of the yield curve situation, so too is Federal Reserve Chair Jay Powell. On Monday, the 10-year yield stood at 2. They would prefer to buy long-term bonds and tie up their money for years even though they receive lower yields. A bond yield is the return an investor gets on a government or corporate bond.
Next
Inverted Yield Curve: what is it and how does it predict disaster?
Eventually, the yield on short-term Treasurys rises higher than the yield on long-term bonds and the yield curve inverts. By early December 1988, the curve had inverted. Why does Wall Street care so much? It is perfectly rational to expect interest rates to fall during recessions. If people want longer term stability, they will seek longer-term Treasuries, as a virtually risk-free investment. It takes a little bit of science and art!!! As an investor, the best thing you can do next time you hear an inverted yield curve story is to ignore it and go play with your grandchildren. Analysts and investors alike place great value in the yield spread, but for those unfamiliar with the indicator, headlines can be confusing and vague.
Next





.1566488000880.png)

