Tilt test. Tilt Test 2019-11-22
Talar Tilt

General recommendations independent of protocol: The test should be performed in a quiet room with the lights slightly dimmed. The tilt test is also known as a tilt table test because it involves being basically strapped to a table that can tilt to different angles. Coronary vasospasm induced during isoproterenol head-up tilt test. The syncopal episodes begin later in life, suggesting that they occur as a result of some underlying progressive dysfunction. Normally, these cardiovascular adjustments occur very quickly, and you shouldn't have a significant drop in your blood pressure. What happens after the test? What is a Tilt Test? Fainting may also be called syncope.
Next
The Talar Tilt Test
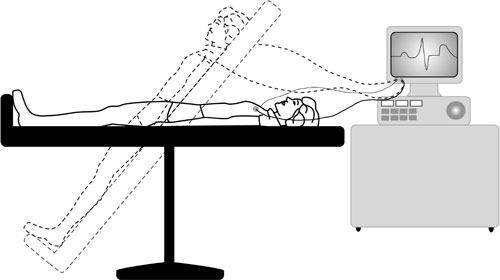
Upright tilt table testing in the evaluation of syncope. Risks A tilt table test is generally safe, and complications are rare. Check with your physician to see if any of your medications need to be held. This is extremely important because there is effective treatment for the condition which can either totally eradicate or dramatically reduce the frequency and intensity of symptoms dizziness and black out spells. Role of endogenous opiods in syncope induced by head-up tilt test and its relationship with isoproterenol-dependent and isoproterenol-independentneurally-mediated syncope. Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown Importance of Test: When assessing inversion and eversion motion at the ankle, you are describing motion that occurs parallel to the frontal plane This motion is not to be confused with supination, which is a combination of inversion, adduction, and plantar flexion.
Next
Tilt Table Test: Uses, Side Effects, Procedure, Results

A randomized trial of the contribution of a drug-free phase and a nitroglycerin phase in the diagnosis of neurally mediated syncope. What you need to know about your test results: Your healthcare provider will discuss your test results with you. Experienced staff and equipment are on hand to handle these potential complications. The examiner then determines how much inversion is present. The need to have a physician continuously present during the test has not been well established.
Next
Tilt

Most of the tests initially performed on these patients mostly in general practices and not in dedicated syncope units do not yield any positive results. If your test is positive you may experience all the usual sensations you experience during a natural episode. If you have syncope, your healthcare provider will carefully evaluate your past medical history and do a physical exam. Your heart rate and blood pressure will be monitored. . Have someone else drive you home if you fainted during the test.
Next
Tilt Test
Risks of a tilt table test: You may feel dizzy, have an irregular or fast heartbeat, or low blood pressure during the test. Please check in at the at your scheduled appointment time. An appointment will then be made for you to return to discuss the results of the test and any treatment options that may be needed. If you do lose consciousness this normally only lasts for a short period of time and the bed is lowered whilst you recover. Reliability of quantifiable tilt table data.
Next
Tilt table test

Your heart rate and blood pressure will be monitored in each position to evaluate your body's cardiovascular response to the change in position. Recently, i received a new pacemaker as the battery in the original expired. The procedure that we now follow was given by Marshall M. You may need to arrange for someone to drive you. The table then creates a change in posture from lying to standing. A Tilt test allows the doctor to monitor your blood pressure and heart rhythm when you are lying down and standing up. You may also need to pay a co-pay, and the facility can provide you with this information as well.
Next
Parks

Surprisingly, the majority of the patients never sustain serious injuries and the diagnosis may go undetected for decades. This is a motorized table with a metal footboard. What happens just before the test? To understand this phenomenon, we must first examine how the nervous system of the body functions. We recently reported our experience with this protocol based on data of 426 patients sensitivity of 67. If your doctor is not the same person who did your tilt table test, then your doctor will need to review that report and assess it in combination with your symptoms and medical history to be able to discuss a diagnosis and plan with you. If you are seeing this message, it is likely that the Javascript option in your browser is disabled.
Next
Tilt Table Test: Uses, Side Effects, Procedure, Results

Who Should Undergo Tilt-Table Testing? Test Position: Supine or sitting. What will happen during a tilt table test: You will need to stay on your back for the entire test. Rarely, this test may cause you to faint. Another problem with tilt tests is that the results recorded. Your doctor may recommend other forms of testing to monitor your heart, such as a Holter monitor you wear to track your heart rate over time. It is important to move as little as possible during the test.
Next
Parks

Your doctor might ask you to stop taking those that alter your heart rate or blood pressure for a day or so before the test, but, because the evaluation of unexplained syncope is so complex and individualized, there is no hard and fast rule about this. If you do not have a meter, please let us know so we can give you one to use. Your healthcare provider will give you instructions as to how long you should withhold food or liquids. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. The purpose of the test is not to make you faint, although you may, depending on how you respond to the test. What happens during the tilt table test? You may also wish to bring a change of clothes as some people may very occasionally experience loss of bladder control during the test.
Next
Tilt Test Explained! MyHeart

Can I eat before the test? Syncope is defined as the sudden loss of consciousness and postural tone with spontaneous recovery. How do I get ready for the tilt table test? The arm cuff will check your blood pressure every 4 to 10 minutes. Usefulness of a tilt training program for the prevention of refractory neurocardiogenic syncope in adolescents: a controlled study. This method results in a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 85%. Resolution of symptoms can take seconds or hours. The problem with neurally mediated syncope is that there is no clear definition of what it is! Take your prescription medications as you normally would, with small sips of water. Syncope transient loss of consciousness due to transient global cerebral hypoperfusion characterized by rapid onset, short duration and spontaneous complete recovery is a very common condition.
Next









